PSAT 10 Math Formulas
Are you preparing for your PSAT 10 Math test this school year? First, understand that the PSAT 10 Mathematics test includes a formula sheet. This means there will be formulas relating to geometric, measurement and some algebra concepts. The exam also includes plenty of application questions; however, the math formulas themselves are not provided in advance so it is up to you to apply them yourself! You will have access many different types of math problem on your PSAT 10 Exam but it's important that all these topics come back quickly when needed as well as put together a list of all "necessary" content knowledge before taking part in any question.
Below we provide our own list: Math Formulas and their meaning - keep this around for quick reference when necessary- review first then take an overview on what needs applying.
The PSAT 10 Math test includes a formula sheet, which displays formulas relating to geometric, measurement and some algebra concepts. You have an opportunity to focus on the application of these formulas rather than their memorization in order to succeed on this exam. However, there is no list of all math formulas that will be required for you so that you must recall many math formulas during your exam time!
Some formulas are provided for you on the PSAT 10 Math test to help with memorization, but it's not a list of every formula that will be required - so use this sheet as a quick reminder when you forget one! Review them all and then apply them..
$76.99 $36.99
52% Off*
Includes PSAT Math Prep Books, Workbooks, and Practice Tests
Place Value
The value of the place, or position, of a digit in a number.
Example: In 456, the 5 is in “tens” position.
Fractions
A number expressed in the form \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Adding and Subtracting with the same denominator:
\(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{b}=\frac{a+c}{b}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}-\frac{c}{b}=\frac{a-c}{b}\)
Adding and Subtracting with the different denominator:
\(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{d}=\frac{ad+cb}{bd}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}-\frac{c}{d}=\frac{ad-cb}{bd}\)
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions:
\(\frac{a}{b} × \frac{c}{d}=\frac{a×c}{b×d}\)
\(\frac{a}{b} ÷ \frac{c}{d}=\frac{\frac{a}{b}}{\frac{c}{d}}=\frac{ad}{bc}\)
Comparing Numbers Signs
Equal to \(=\)
Less than \( <\)
Greater than \(>\)
Greater than or equal \(≥\)
Less than or equal \(≤\)
Rounding
Putting a number up or down to the nearest whole number or the nearest hundred, etc.
Example: 64 rounded to the nearest ten is 60 , because 64 is closer to 60 than to 70.
Whole Number
The numbers \( \{0,1,2,3,…\} \)
Estimates
Find a number close to the exact answer.
Decimals
Is a fraction written in a special form. For example, instead of writing \(\frac{1}{2}\) you can write \(0.5\).
Mixed Numbers
A number composed of a whole number and fraction. Example: \(2 \frac{2}{ 3}\) Converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers: \(a \frac{c}{b}=a+\frac{c}{b}= \frac{ab+ c}{b}\)
Factoring Numbers
Factor a number means to break it up into numbers that can be multiplied together to get the original number. Example:\(12=2×2×3\)
Divisibility Rules
Divisibility means that you are able to divide a number evenly. Example: 24 is divisible by 6, because \(24÷6=4\)
Greatest Common Factor
Multiply common prime factors
Example:\( 200=2×2×2×5×5 60=2×2×3×5\)
GCF \((200,60)=2×2×5=20\)
Least Common Multiple
Check multiples of the largest number
Example: LCM (200, 60): 200 (no), 400 (no), 600 (yes!)
Integers
\( \{…,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,…\} \)
Includes: zero, counting numbers, and the negative of the counting numbers
Real Numbers
All numbers that are on number line. Integers plus fractions, decimals, and irrationals etc.) (\(\sqrt{2},\sqrt{3},π\), etc.)
Order of Operations
PEMDAS
(parentheses / exponents / multiply / divide / add / subtract)
Absolute Value
Refers to the distance of a number from , the distances are positive as absolute value of a number cannot be negative. \(|-22|=22\)
or \(|x| =\begin{cases}x \ for \ x≥0 \\x \ for \ x < 0\end{cases} \)
\(|x|<n⇒-n<x<n\)
\(|x|>n⇒x<-n \ or \ x>n\)
Ratios
A ratio is a comparison of two numbers by division.
Example: \(3 : 5\), or \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Percentages
Use the following formula to find part, whole, or percent
part \(=\frac{percent}{100}×whole\)
Proportional Ratios
A proportion means that two ratios are equal. It can be written in two ways:
\(\frac{a}{b}=\frac{c}{d}\) , \(a: b = c: d \)
Percent of Change
\(\frac{New \ Value \ – \ Old \ Value}{Old Value}×100\%\)
Markup
Markup \(=\) selling price \(–\) cost
Markup rate \(=\) markup divided by the cost
Discount
Multiply the regular price by the rate of discount
Selling price \(=\) original price \(–\) discount
Expressions and Variables
A variable is a letter that represents unspecified numbers. One may use a variable in the same manner as all other numbers:
Addition: \(2+a\) : \(2\) plus a
Subtraction: \(y-3\) : \(y\) minus \(3\)
Division: \(\frac{4}{x}\) : 4 divided by x
Multiplication: \(5a\) : \(5\) times a
Tax
To find tax, multiply the tax rate to the taxable amount (income, property value, etc.)
$24.99 $14.99
40% Off*
The Ultimate Step by Step Guide to Preparing for the PSAT Math Test
Polynomial
\(P(x)=a_{0} x^n+ a_{1} x^{n-1}+\)⋯\(+a_{n-2} x^2+a_{n-1} x+an\)
Equations
The values of two mathematical expressions are equal.
\(ax+b=c\)
Systems of Equations
Two or more equations working together.
example: \( \begin{cases}-2x \ + \ 2y \ =4\\-2x \ + \ y \ = \ 3\end{cases} \)
Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution
Consider the system of equations: \( \begin{cases}x \ - \ y \ = \ 1\\-2x \ + \ y \ = \ 6\end{cases} \)
Substitute \(x \ = \ 1 \ - \ y\) in the second equation: \(-2(1 \ - \ y) \ + \ y \ = \ 5 \ ⇒ \ y \ = \ 2\)
Substitute \(y \ = \ 2\) in \(x \ = \ 1 \ + \ y\) \(⇒ \ x \ = \ 1 \ + \ 2 \ = \ 3\)
Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination
Example:
\(\cfrac{\begin{align} x+2y =6 \\ + \ \ -x+y=3 \end{align}}{}\)
\(\cfrac{ \begin{align} 3y=9 \\ y=3 \end{align} }{\begin{align} x+6=6 \\ ⇒ x=0 \end{align}} \)
Functions
A function is a rule to go from one number (x) to another number (y), usually written \(y=f(x)\).For any given value of x, there can only be one corresponding value y. If \(y=kx\) for some number k (example: \(f(x)= 0.5 x\)), then y is said to be directly proportional to x. If y\(=\frac{k}{x }\) (example: f(x \(=\frac{5}{x}\)), then y is said to be inversely proportional to x. The graph of \(y=f(x )+k\) is the translation of the graph of \(y=f(x)\) by \((h,k)\) units in the plane. For example, \(y=f(x+3)\) shifts the graph of \(f(x)\) by 3 units to the left.
Inequalities
Says that two values are not equal
\(a≠b\) a not equal to b
\(a<b\) a less than b
\(a>b\) a greater than b
\(a≥b\) a greater than or equal b
\(a≤b\) a less than or equal b
Lines (Linear Functions)
Consider the line that goes through points \(A(x_{1},y_{1}) \) and \(B(x_{2},y_{2})\).
Distance from A to B:
\(\sqrt{(x_{1}-x_{2})^2+(y_{1}-y_{2})^2 }\)
Parallel and Perpendicular lines:
Have equal slopes. Perpendicular lines (i.e., those that make a \(90^° \) angle where they intersect) have negative reciprocal slopes: \(m_{1}\) .\(m_{2}=-1\).
Parallel Lines (l \(\parallel\) m)
Mid-point of the segment AB:
M (\(\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}}{2} , \frac{y_{1}+y_{2}}{2}\))
Slope of the line:
\(\frac{y_{2}- y_{1}}{x_{2} – x_{1} }=\frac{rise}{run}\)
Point-slope form:
Given the slope m and a point \((x_{1},y_{1})\) on the line, the equation of the line is
\((y-y_{1})=m \ (x-x_{1})\).
Intersecting lines:
Opposite angles are equal. Also, each pair of angles along the same line add to \(180^°\). In the figure above, \(a+b=180^°\).
Slope-intercept form:
given the slope m and the y-intercept b, then the equation of the line is:
\(y=mx+b\).
Transversal: Parallel lines:
Eight angles are formed when a line crosses two parallel lines. The four big angles (a) are equal, and the four small angles (b) are equal.
Parabolas:
A parabola parallel to the y-axis is given by \(y=ax^2+bx+c\).
If \(a>0\), the parabola opens up.
If \(a<0\), the parabola opens down. The y-intercept is c, and the x-coordinate of the vertex is: \(x=-\frac{b}{2a}\).
Factoring:
“FOIL”
\((x+a)(x+b)\)
\(=x^2+(b+a)x +ab\)
“Difference of Squares”
\(a^2-b^2= (a+b)(a-b)\)
\(a^2+2ab+b^2=(a+b)(a+b) \)
\(a^2-2ab+b^2=(a-b)(a-b)\)
“Reverse FOIL”
\(x^2+(b+a)x+ab=\) \((x+a)(x+b)\)
You can use Reverse FOIL to factor a polynomial by thinking about two numbers a and b which add to the number in front of the x, and which multiply to give the constant. For example, to factor \(x^2+5x+6\), the numbers add to 5 and multiply to 6, i.e.:
\(a=2\) and \(b=3\), so that \(x^2+5x+6=(x+2)(x+3)\).
To solve a quadratic such as \(x^2+bx+c=0\), first factor the left side to get \((x+a)(x+b)=0\), then set each part in parentheses equal to zero.
For example, \(x^2+4x+3= (x+3)(x+1)=0\) so that \(x=-3\) or \(x=-1\).
To solve two linear equations in x and y: use the first equation to substitute for a variable in the second. E.g., suppose \(x+y=3\) and \(4x-y=2\). The first equation gives y=3-x, so the second equation becomes \(4x-(3-x)=2 ⇒ 5x-3=2\) \(⇒ x=1,y=2\).
Exponents:
Refers to the number of times a number is multiplied by itself.
\(8 = 2 × 2 × 2 = 2^3\)
Scientific Notation:
It is a way of expressing numbers that are too big or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form.
In scientific notation all numbers are written in this form: \(m \times 10^n\)
| Decimal notation |
Scientific notation |
| 5 |
\(5×10^0\) |
| \(-25,000\) |
\(-2.5×10^4\) |
| 0.5 |
\(5×10^{-1}\) |
| 2,122.456 |
\(2,122456×10^3\) |
Square:
The number we get after multiplying an integer (not a fraction) by itself. Example: \(2×2=4,2^2=4\)
Square Roots:
A square root of \(x\) is a number r whose square is \(x : r^2=x\)
\(r\) is a square root of \(x\)
Pythagorean Theorem:
\(a^2+b^2=c^2\)
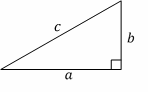
Triangles
Right triangles:
A good example of a right triangle is one with a=3, b=4, and c=5, also called a \( 3-4-5\) right triangle. Note that multiples of these numbers are also right triangles. For example, if you multiply these numbers by 2, you get a=6, b=8 and
\(c=10(6-8-10)\), which is also a right triangle.
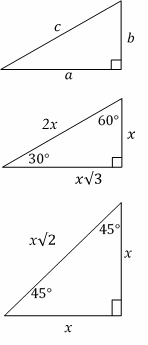
All triangles:
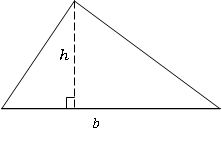
Area \(=\frac{1}{2}\) \(b \times h\)
Angles on the inside of any triangle add up to \(180^\circ\).
The length of one side of any triangle is always less than the sum and more than the difference of the lengths of the other two sides.
An exterior angle of any triangle is equal to the sum of the two remote interior angles. Other important triangles:
Equilateral:
These triangles have three equal sides, and all three angles are \(60^\circ\).
Isosceles:
An isosceles triangle has two equal sides. The “base” angles (the ones opposite the two sides) are equal (see the \(45^\circ\) triangle above).
$76.99 $36.99
52% Off*
Includes PSAT Math Prep Books, Workbooks, and Practice Tests
Similar:
Two or more triangles are similar if they have the same shape. The corresponding angles are equal, and the corresponding sides are in proportion. For example, the \(3-4-5\) triangle and the \(6-8-10\) triangle from before are similar since their sides are in a ratio of \(2\) to \(1\).
Circles
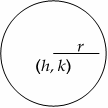
Area \(=πr^2\)
Circumference \(=2πr\)
Full circle \(=360^\circ\)
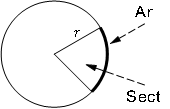
Length Of Arc \(= \ \frac{n°}{360°} \times 2πr\)
Area Of Sector \(= \ \frac{n°}{360°} \times πr^2\)
Equation of the circle (above left figure): \((x \ - \ h)^2 \ + \ (y \ - \ k)^2 \ = \ r^2\).
Rectangles
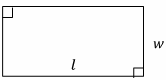
(Square if l=w)
Area=lw
Parallelogram
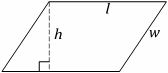
(Rhombus if l=w)
Area=lh
Regular polygons are n-sided figures with all sides equal and all angles equal.
The sum of the inside angles of an n-sided regular polygon is
\((n-2) .180^\circ\).
Area of a trapezoid:
\(A =\frac{1}{2} \ h (b_{1}+b_{2})\)
Surface Area and Volume of a rectangular/right prism:
Surface Area and Volume of a cylinder:
\(SA =2πrh+2πr^2\)
\(V =πr^2 h \)
Surface Area and Volume of a Pyramid
\(SA=\frac{1}{2} \ ps+b\)
\(V=\frac{1}{3}\ bh\)
Surface Area and Volume of a Cone
\(SA =πrs+πr^2\)
\(V=\frac{1}{3} \ πr^2 \ h\)
Surface Area and Volume of a Sphere
\(SA =4πr^2\)
\(V =\frac{4}{3} \ πr^3\)
(p \(=\) perimeter of base B; \(π ~ 3.14 \))
Solids
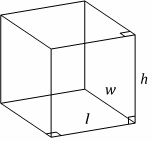
Rectangular Solid
Volume \(= \ l \times w \times h\)
Area \(= \ 2(lw \ + \ wh \ + \ lh)\)
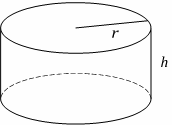
Right Cylinder
Volume \(= \ πr^2 \ h\)
Area \(= \ 2πr \ (r \ + \ h)\)
Quadratic formula:
\( x=\frac{-b±\sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}\)
Simple interest:
\(I=prt\)
(I = interest, p = principal, r = rate, t = time)
mean:
mean: \(\frac{sum \ of \ the \ data}{of \ data \ entires}\)
mode:
value in the list that appears most often
range:
largest value \(-\) smallest value
Median
Middle value in the list (which must be sorted)
Example: median of
\( \{3,10,9,27,50\} = 10\)
Example: median of
\( \{3,9,10,27\}=\frac{(9+10)}{2}=9.5 \)
Sum
average \(×\) (number of terms)
Average
\( \frac{sum \ of \ terms}{number \ of \ terms}\)
Average speed
\(\frac{total \ distance}{total \ time}\)
Probability
\(\frac{number \ of \ desired \ outcomes}{number \ of \ total \ outcomes}\)
The probability of two different events A and B both happening is:
P(A and B)=p(A) .p(B)
as long as the events are independent (not mutually exclusive).
Powers, Exponents, Roots
\(x^a .x^b=x^{a+b}\)
\(\frac{x^a}{x^b} = x^{a-b}\)
\(\frac{1}{x^b }= x^{-b}\)
\((x^a)^b=x^{a.b}\)
\((xy)^a= x^a .y^a\)
\(x^0=1\)
\(\sqrt{xy}=\sqrt{x} .\sqrt{y}\)
\((-1)^n=-1\), if n is odd.
\((-1)^n=+1\), if n is even.
If \(0<x<1\), then
\(0<x^3<x^2<x<\sqrt{x}<\sqrt{3x}<1\).
Interest
Simple Interest
The charge for borrowing money or the return for lending it.
Interest = principal \(×\) rate \(×\) time
OR
\(I=prt\)
Compound Interest
Interest computed on the accumulated unpaid interest as well as on the original principal.
A \(=P(1+r)^t\)
A= amount at end of time
P= principal (starting amount)
r= interest rate (change to a decimal i.e. \(50\%=0.50\))
t= number of years invested
Powers / Exponents
Positive Exponents
An exponent is simply shorthand for multiplying that number of identical factors. So \(4^3\) is the same as (4)(4)(4), three identical factors of 4. And \(x^3\) is just three factors of x, \((x)(x)(x)\).
Negative Exponents
A negative exponent means to divide by that number of factors instead of multiplying.
So \(4^{-3}\) is the same as \( \frac{1}{4^3}\) and
\(x^{-3}=\frac{1}{x^3}\)
Factorials
Factorial- the product of a number and all counting numbers below it.
8 factorial \(=8!=\)
\(8×7×6×5×4×3×2×1=40,320\)
5 factorial \(=5!=\)
\(5×4×3×2×1=120\)
2 factorial \(=2!=2× 1=2\)
Multiplying Two Powers of the SAME Base
When the bases are the same, you find the new power by just adding the exponents
\(x^a .x^b=x^{a+b }\)
Multiplying Two Powers of Different Bases Same Exponent
If the bases are different but the exponents are the same, then you can combine them
\(x^a \times y^a \ = \ (xy)^a\)
Powers of Powers
For power of a power: you multiply the exponents.
\((x^a)^b=x^{(ab)}\)
Dividing Powers
\(\frac{x^a}{x^b} =x^a x^{-b}= x^{a-b}\)
The Zero Exponent
Anything to the 0 power is 1.
\(x^0= 1\)
Permutation:
When different orderings of the same items are counted separately, we have a permutation problem:
\(_{n}P_{r}=\frac{n!}{(n-1)!}\)
Combination:
The fundamental counting principle, as demonstrated above, is used any time the order of the outcomes is important. When selecting objects from a group where the order is NOT important, we use the formula for COMBINATIONS:
The fundamental counting principle, as demonstrated above, is used any time the order of the outcomes is important. When selecting objects from a group where the order is NOT important, we use the formula for COMBINATIONS:
\(_{n}C_{r}=\frac{n!}{r!(n-1)!}\)
$24.99 $14.99
40% Off*
The Ultimate Step by Step Guide to Preparing for the PSAT Math Test
The Six Trig Ratios
Values for the common angles
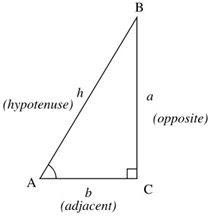
\(Sin(θ) \ = \ \frac{opp_.}{hip_.}\) \(Csc(θ) \ = \ \frac{hip_.}{opp}\)
\(Cos(θ) \ = \ \frac{adj}{hip_.}\) \(Sec(θ) \ = \ \frac{hip}{adj}\)
\(tan(θ) \ = \ \frac{opp_.}{adj_.}\) \(tan(θ) \ = \ \frac{adj}{opp_.}\)
Trig Functions relationships
\(Tan(x) \ = \ \frac{Sin(x)}{Cos(x)}\)
\(Csc(x) \ = \ \frac{1}{Sin(x)}\)
\(Sec(x) \ = \ \frac{1}{Cos(x)}\)
\(Cot(x) \ = \ \frac{Cos(x)}{Sin(x)} \ = \ \frac{1}{Tan(x)}\)
You May Also Like to Read
More Articles